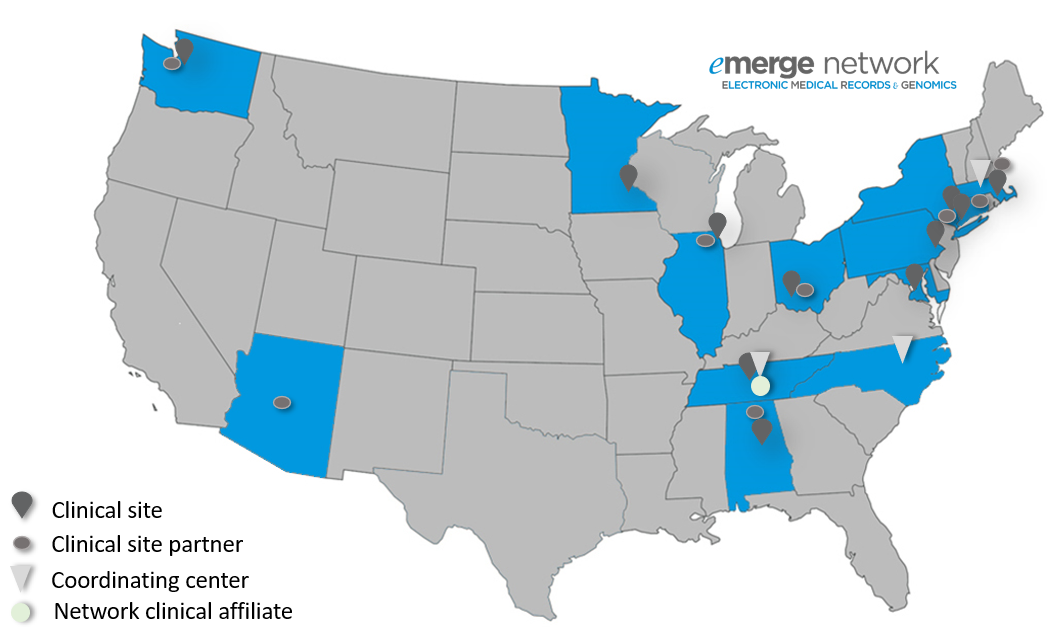
eMERGE is a national network organized and funded by the
National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) that combines DNA
biorepositories with electronic medical record (EMR) systems for large
scale, high-throughput genetic research in support of implementing genomic
medicine.
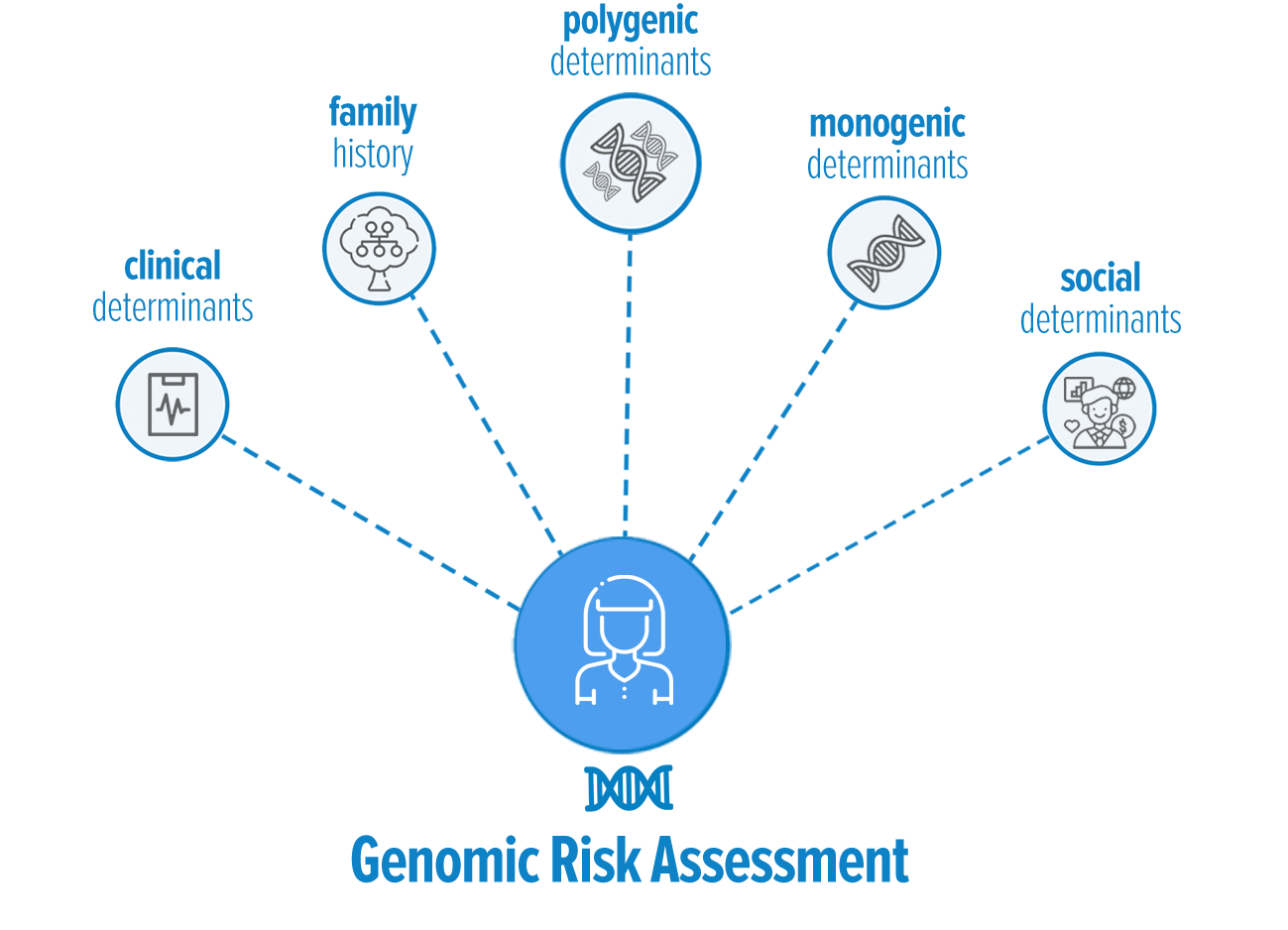
Many factors contribute to risk of a disease. Some of these factors are internal,
like genetics, and others are external, like where someone lives. Over the last several years
researchers have discovered that in addition to one gene being associated with a given
disease (monogenic factors), many genes across your genome can contribute to the development
of a disease (polygenic factors). To learn more about elements that contribute to risk a disease,
click here.
Latest News
RFI: Updated Genomic Data Sharing Policy
January 1, 2026 4:31 PM
NIH Notice: Updated Biosketch and OS Format
January 1, 2026 4:30 PM
NIH Loan Repayment Program (LRP) Update
August 8, 2025 3:24 PM
ELSI Revised NOFOs
April 4, 2025 2:34 PM
DEADLINE EXTENDED, Now April 14th: NCI/AcademyHealth Visiting Scholars Program
March 3, 2025 9:41 PM
Inviting Feedback on the Framework for the NIH Strategic Plan for Disability Health Research FY26-FY30
January 1, 2025 7:38 PM
Recent Publications
Strom NI, Verhulst B, Bacanu SA, Cheesman R, Hettema JM, et al. Genome-wide association study of major anxiety disorders in 122,341 European-ancestry cases identifies 58 loci and highlights GABAergic signaling. Nature genetics. 2026 Feb;58(2):275-288.
Brokamp E, Scalici A, Miller-Fleming T, Wu D, Shuey MM. Expanding the Genetic Landscape of Craniofacial Anomalies Through Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies. Research square. 2025 Dec 30;.
Zhong X, Jia G, Yin Z, Chen R, Cox NJ. Longitudinal analysis of electronic health records reveals medical conditions associated with subsequent Alzheimer's disease development. Alzheimer's research & therapy. 2025 Dec 29;17(1):263.